User Management
By Infinium August 6, 2023
User Management is a crucial process within any system or organization that involves managing user accounts, access, roles, and permissions. It ensures that individuals can interact with a system or network securely and effectively, while safeguarding sensitive data and resources. User management is vital for maintaining security, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance across various platforms, from corporate environments to web applications.
Key Objectives of User Management
- Access Control: Ensuring that users have appropriate access to systems, applications, and data based on their role or function.
- User Authentication: Verifying the identity of users to ensure that only authorized individuals gain access to the system.
- User Provisioning: Adding, configuring, and managing new user accounts, assigning them proper roles and permissions.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Keeping track of user activities to identify potential security risks or misuse of resources.
- Password Management: Enforcing password policies, including creation, updates, and resets, to ensure security.
Components of User Management
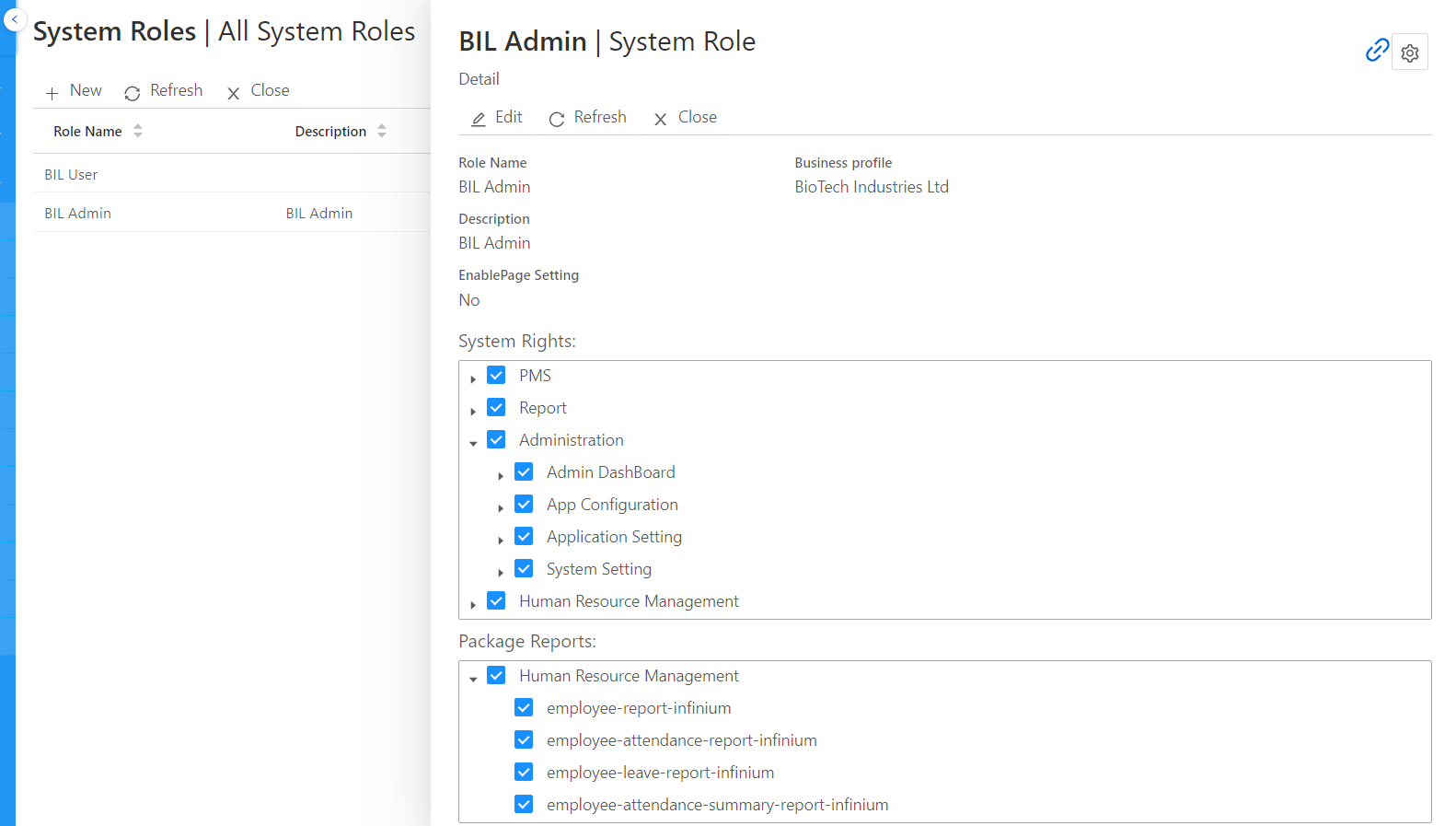
User Roles and Permissions: User management defines roles within the system (e.g., admin, editor, viewer) and assigns specific permissions to control access. For example:
- Admin: Has full access, including user management and system settings.
- Editor: Can modify content but has limited access to system configuration.
- Viewer: Can view data or content but cannot make changes.
User Authentication: Methods for confirming user identity, typically involving credentials like usernames and passwords. More advanced authentication methods include:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds a second layer of security by requiring additional verification (e.g., SMS code, fingerprint).
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Allows users to log in with one set of credentials across multiple systems.
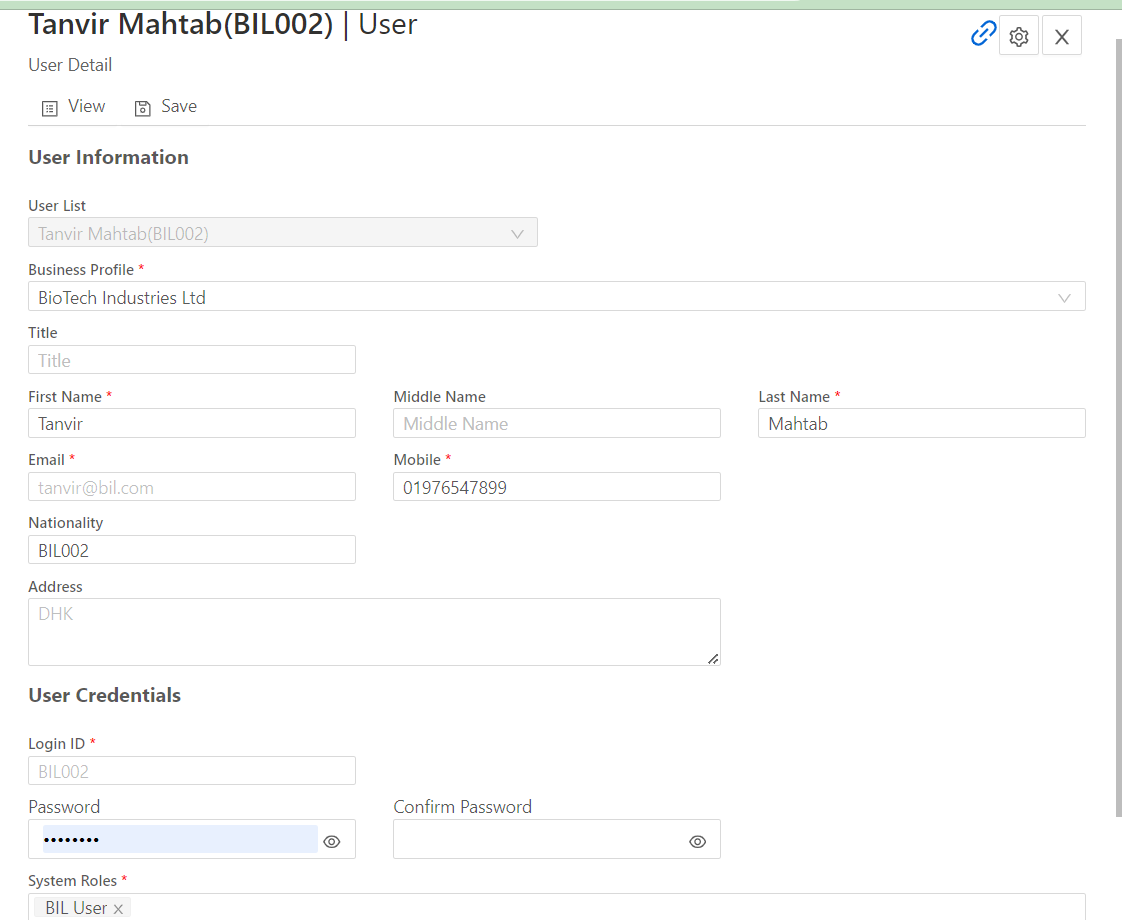
User Provisioning and Deprovisioning: The process of creating new accounts for users, assigning them appropriate roles, and deactivating or deleting accounts when no longer needed. It includes:
- Setting access controls upon onboarding.
- Disabling accounts when users leave the organization.
User Activity Monitoring: Tracking and logging user activities, such as login attempts, data access, or changes made within the system, to ensure compliance and detect potential security threats.
Self-Service Features: Enabling users to manage their own profiles, such as updating personal information or resetting passwords, reduces administrative workload.
Group Management: Organizing users into groups (e.g., departments, teams) to streamline permissions and ensure consistent access levels for multiple users.
Types of User Management
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Users are assigned roles with predefined permissions, making access management simple and efficient.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): Access permissions are granted based on attributes (e.g., job title, department), offering more granular control over user access.
Centralized User Management: All user accounts are managed from a central system, allowing for consistent enforcement of security policies across the organization.
Decentralized User Management: Each department or team manages its own users and permissions, providing more localized control but potentially leading to inconsistent policies.
Principles of User Management
- Least Privilege: Users should be given the minimum necessary access to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or accidental data exposure.
- Separation of Duties: Tasks are divided among users to ensure no single user has excessive control over critical processes.
- Audit and Compliance: Regular reviews of user access and activities are essential for ensuring compliance with security policies and regulations.
Importance of User Management
- Enhanced Security: Proper user management protects systems from unauthorized access and helps prevent data breaches.
- Operational Efficiency: By automating tasks like user provisioning and password resets, organizations can save time and reduce manual errors.
- Regulatory Compliance: User management ensures adherence to legal and regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) by controlling access to sensitive information.
- User Accountability: By monitoring and logging user actions, organizations can identify misuse or unauthorized behavior, fostering accountability.
Users of User Management Systems
- Administrators: Set up user accounts, manage access permissions, and ensure system security.
- End Users: Employees or customers who need access to specific resources or data.
- Security Teams: Monitor user activities and ensure that policies are being followed to prevent security incidents.
- IT Departments: Oversee user management to maintain system integrity and facilitate smooth operations.
Challenges in User Management
- Managing Multiple Systems: With many organizations using several applications, managing user access across platforms can be complex.
- User Lifecycle Management: Ensuring timely deactivation of accounts when employees leave can be overlooked, leading to potential security risks.
- Balancing Security and Usability: Strong security measures like multi-factor authentication can sometimes hinder user experience, making it challenging to find the right balance.
- Password Management Issues: Users often struggle with remembering multiple complex passwords, leading to poor password hygiene or reliance on insecure password practices.
Conclusion
User Management is essential for any organization that deals with multiple users or systems. By implementing strong user management practices, organizations can enhance security, streamline operations, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Proper user management fosters accountability and helps reduce the risk of security breaches, while also ensuring that users have access to the resources they need for their roles.

Interested in what Infinium Suite can do for you?
Links
Contact Us
- +8801714-042726
- info@infiniumsuite.com
- Morning Glory, Concord Colosseum, House# 19 Road No 13C, Dhaka 1213
