Point of Sale (POS)
By Infinium August 6, 2023
A Point of Sale (POS) system is a combination of hardware and software that businesses use to conduct sales transactions. It serves as the central hub where customers complete their purchases, and businesses process payments. Modern POS systems offer much more than just transaction processing—they also provide tools for inventory management, customer relationship management, sales tracking, and analytics. A POS system can be used in various industries, including retail, hospitality, and restaurants, to streamline operations and enhance customer experience.
Components of a POS System
Hardware: The physical devices needed to complete sales transactions, including:
- POS Terminal: A computer or tablet that runs the POS software and handles the transaction process.
- Cash Register: A drawer for storing cash securely.
- Card Reader: For accepting debit and credit card payments, including contactless and mobile payments.
- Barcode Scanner: Used to scan product barcodes for quick and accurate data entry.
- Receipt Printer: Prints receipts for customers at the end of a transaction.
Software: The system’s core, handling the processing of sales, tracking inventory, managing customer data, and generating reports. It includes:
- Sales Processing: Allows businesses to calculate totals, taxes, discounts, and finalize payments.
- Inventory Management: Tracks stock levels in real-time and automatically updates when a sale is made.
- Employee Management: Allows for managing employee shifts, roles, and performance.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Stores customer data to help with personalized service and marketing.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides insights into sales trends, employee performance, and inventory turnover.
Payment Processing: POS systems integrate with payment gateways to securely process various forms of payment, including cash, credit/debit cards, digital wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay), and gift cards.
Types of POS Systems
Cloud-Based POS: These systems store data on the cloud, allowing access from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud POS systems are scalable, flexible, and typically require minimal hardware.
- Advantages: Remote access, automatic updates, and lower upfront costs.
- Disadvantages: Requires an internet connection to operate effectively.
On-Premises POS: Installed on local servers, these systems offer full control over data but may require more hardware and maintenance.
- Advantages: More control over data and no dependency on internet connectivity.
- Disadvantages: Higher upfront costs and maintenance requirements.
Mobile POS (mPOS): A portable version of a POS system, often used on tablets or smartphones. mPOS systems are popular with small businesses, pop-up shops, and vendors on the go.
- Advantages: Portability and low setup costs.
- Disadvantages: Limited functionality compared to full POS systems.
Multichannel POS: Designed for businesses that sell through multiple channels (e.g., physical stores, online, and mobile). These systems integrate in-store and e-commerce sales data, providing a unified view of operations.
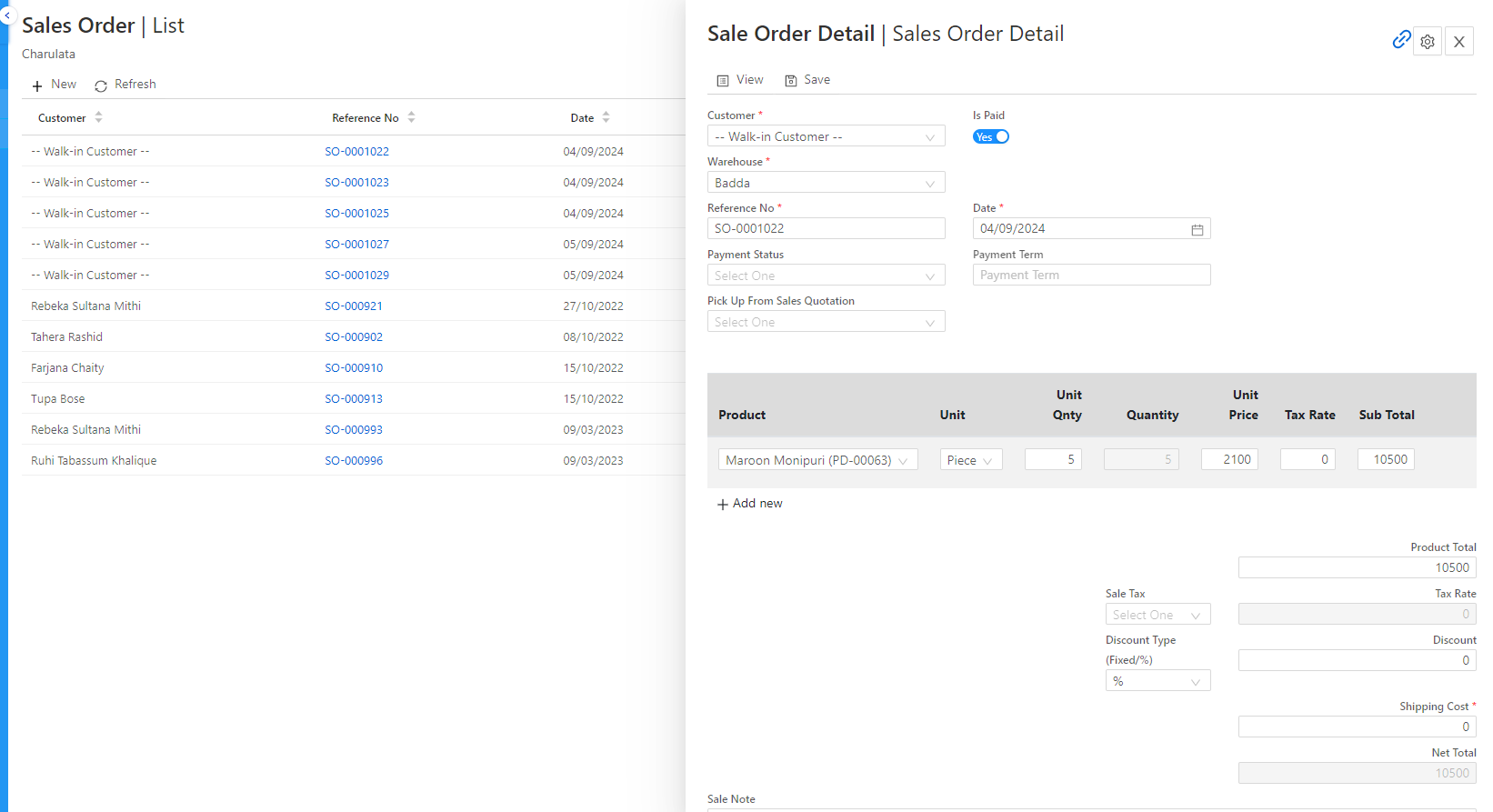
Key Features of a POS System
Sales Processing: The ability to handle multiple types of payments, apply discounts, manage taxes, and process returns/exchanges.
Inventory Management: Track product stock in real-time, receive low-stock alerts, and generate reports on best-selling products and deadstock.
Customer Management: Store customer information, track purchase history, and enable personalized marketing such as loyalty programs, email campaigns, and promotions.
Employee Management: Manage employee permissions, track sales performance, and calculate payroll based on hours worked.
Reporting and Analytics: Access detailed reports on sales, customer behavior, inventory levels, and employee performance to make data-driven decisions.
Multi-Store Management: For businesses with multiple locations, POS systems can sync data across stores, providing a unified view of inventory, sales, and customer data.
Third-Party Integrations: Many POS systems integrate with accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks), e-commerce platforms (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce), and payment processors (e.g., PayPal, Stripe).
Offline Mode: Some POS systems offer offline capabilities, allowing businesses to continue processing sales even without an internet connection.
Benefits of a POS System
Faster Transactions: A POS system speeds up the checkout process by automating calculations and enabling quick payment processing.
Improved Accuracy: By automating sales and inventory management, POS systems reduce human error and ensure accurate tracking of transactions and stock levels.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Faster checkout, personalized service through customer data, and loyalty programs lead to a better overall customer experience.
Inventory Control: Real-time inventory management helps businesses avoid overstocking or running out of popular items, optimizing stock levels and reducing costs.
Data-Driven Insights: Access to sales reports, customer data, and employee performance helps businesses make informed decisions, optimize operations, and increase profitability.
Streamlined Operations: POS systems automate tasks such as sales tracking, reporting, and inventory management, allowing business owners to focus on growth rather than manual tasks.
Scalability: Modern POS systems are scalable and can grow alongside the business, adding new features or integrating with additional software as needed.
Industries That Use POS Systems
Retail: POS systems in retail track inventory, manage pricing, and process transactions. Features like barcode scanning and receipt printing are essential for quick and accurate sales.
Restaurants: Restaurants use POS systems to take orders, manage tables, split bills, and process payments. Some systems integrate with kitchen display systems (KDS) for seamless communication between waitstaff and kitchen staff.
Hospitality: Hotels and resorts use POS systems to manage room bookings, track customer preferences, and process payments for services such as dining or spa treatments.
Healthcare: Medical facilities use POS systems to handle payments for services, track patient billing, and manage supplies.
Service-Based Businesses: Hair salons, fitness centers, and repair shops use POS systems to schedule appointments, track customer preferences, and process payments.
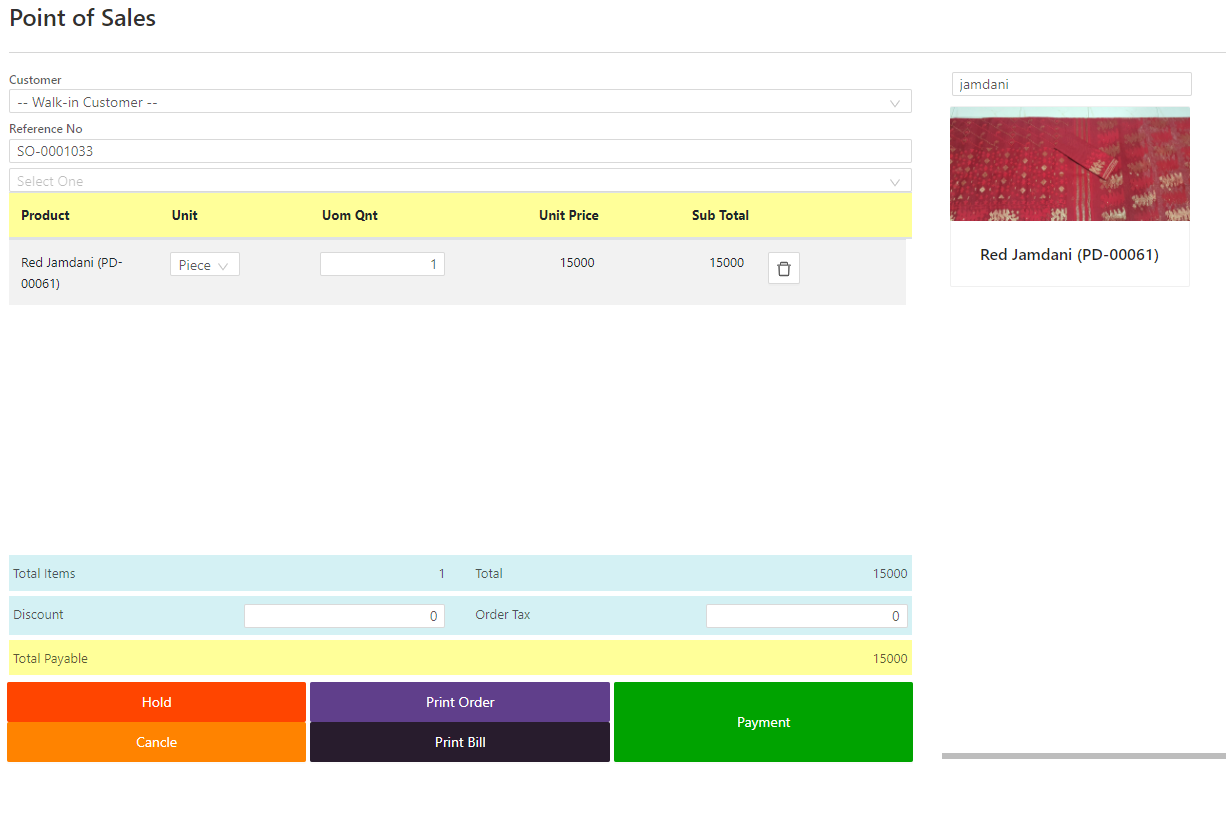
Challenges of a POS System
Initial Costs: The cost of implementing a POS system, especially for hardware and installation, can be high for small businesses.
Training: Employees may need training to use the system efficiently, especially if the POS has complex features or workflows.
Data Security: Storing sensitive customer and payment data comes with security risks. Businesses need to ensure their POS system complies with industry standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
System Downtime: Technical glitches, power outages, or internet issues can cause a POS system to go offline, potentially disrupting sales.
Ongoing Maintenance: Regular updates and maintenance are required to ensure the system remains efficient and secure, which may require additional resources.
Popular POS Systems
Square POS: Known for its simplicity, Square POS is ideal for small businesses and startups. It offers a free plan with basic features and a wide range of integrations.
Shopify POS: Designed for retailers, Shopify POS integrates seamlessly with e-commerce stores, allowing businesses to manage online and in-store sales in one system.
Lightspeed: A robust POS system suitable for retail, restaurants, and hospitality businesses, offering advanced inventory management and analytics.
Toast POS: Tailored specifically for restaurants, Toast POS provides tools for table management, online ordering, and kitchen communication.
Clover POS: A versatile system with customizable hardware options, Clover POS is popular with retailers, restaurants, and service-based businesses.
Conclusion
A Point of Sale (POS) system is essential for modern businesses to streamline transactions, manage inventory, and gain valuable insights into sales and customer behavior. With a variety of POS systems available, businesses can choose a solution that fits their specific needs, whether it’s retail, hospitality, or service-based. By implementing a POS system, businesses can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, and drive growth in an increasingly competitive market.

Interested in what Infinium Suite can do for you?
Links
Contact Us
- +8801714-042726
- info@infiniumsuite.com
- Morning Glory, Concord Colosseum, House# 19 Road No 13C, Dhaka 1213
