Financial Accounting
By Infinium August 6, 2023
Financial accounting is a specialized branch of accounting that deals with the process of recording, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions of a business over a specific period. It provides a clear and structured view of a company’s financial performance and position, allowing stakeholders, including management, investors, creditors, and regulators, to make informed decisions.
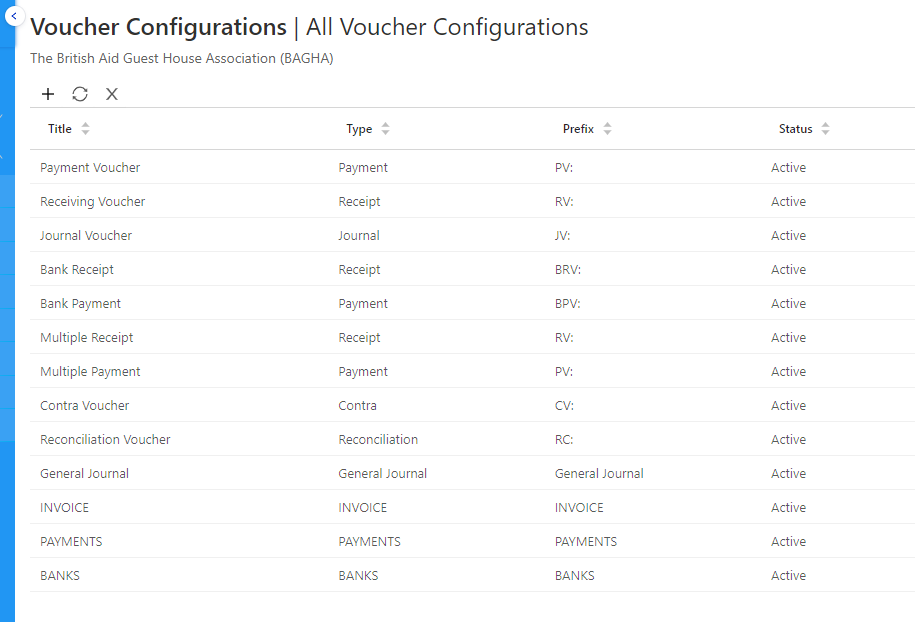
Key Objectives of Financial Accounting
The primary objectives of financial accounting are:
- Recording Financial Transactions: Maintaining a systematic record of all monetary transactions through journals and ledgers.
- Providing Financial Statements: Producing standard reports such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to summarize a company’s financial health.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to national and international accounting standards, such as GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) or IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards).
- Supporting Decision-Making: Offering relevant financial data to stakeholders for informed decision-making.
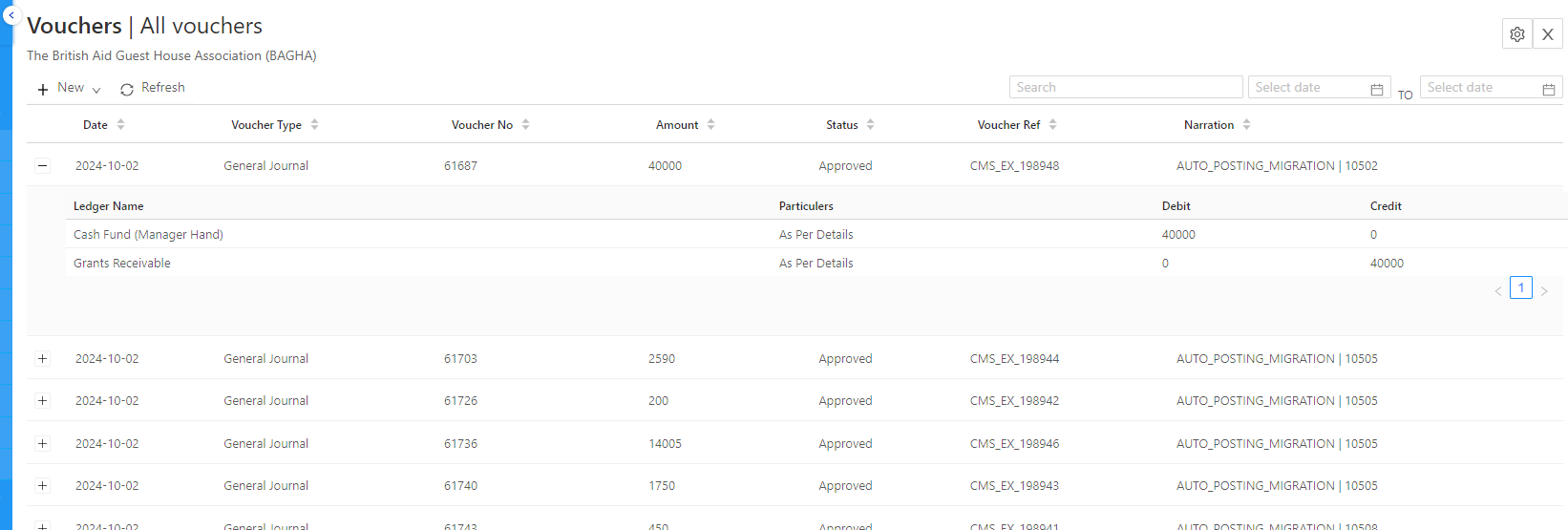
Components of Financial Accounting
Financial Statements: These are the core outputs of financial accounting and include:
- Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement): This shows the company’s profitability over a specific period, detailing revenues, costs, and expenses.
- Balance Sheet: A snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given moment, showing assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- Cash Flow Statement: A record of the company’s cash inflows and outflows over a period, crucial for assessing liquidity.
- Statement of Changes in Equity: It shows changes in the company’s equity over the accounting period.
Double-Entry System: This accounting method records each transaction in two accounts: debit and credit. It ensures that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) remains balanced.
Accrual Basis: In financial accounting, transactions are recorded when they are earned or incurred, not when cash is exchanged. This provides a more accurate representation of financial performance.
Accounting Period: Financial transactions are reported periodically (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually) to provide a continuous record of business activities.
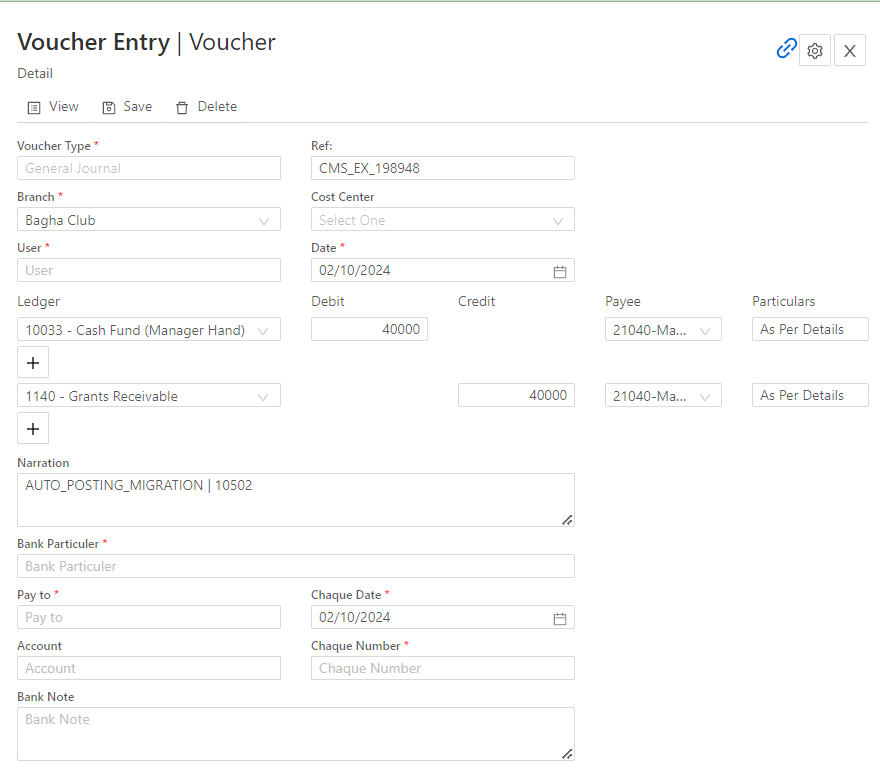
Principles of Financial Accounting
- Revenue Recognition Principle: Revenue is recognized when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received.
- Matching Principle: Expenses should be matched to the revenues they helped generate within the same period.
- Historical Cost Principle: Assets are recorded at their original purchase cost, rather than their current market value.
- Consistency Principle: Once an accounting method is chosen, it should be applied consistently across reporting periods.
- Full Disclosure Principle: All relevant financial information must be disclosed in financial reports.
Importance of Financial Accounting
- Transparency and Trust: Financial accounting promotes transparency by offering a clear view of the company’s financial activities, increasing trust among stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: It helps businesses comply with legal and regulatory requirements by following standardized practices.
- Investor Confidence: Investors rely on accurate financial statements to evaluate a company’s performance and make informed investment decisions.
- Performance Tracking: Financial accounting allows management to track the company’s financial performance, monitor growth, and implement corrective measures when needed.
Users of Financial Accounting Information
- Management: Uses financial data to make strategic decisions, budget, and forecast future performance.
- Investors and Shareholders: Evaluate a company’s profitability and financial health before making investment decisions.
- Creditors and Lenders: Assess the company’s ability to repay debts.
- Regulatory Authorities: Ensure that companies comply with financial reporting standards and regulations.
- Employees: Use financial information to gauge the company’s stability and profitability, affecting their job security and benefits.
Challenges in Financial Accounting
- Complexity in Standards: Adapting to changing accounting standards like IFRS or GAAP can be challenging for companies operating globally.
- Accuracy: Ensuring accurate and error-free financial reporting is crucial but can be time-consuming and requires high attention to detail.
- Regulatory Changes: Frequent changes in tax laws, accounting rules, and financial regulations can complicate the accounting process.
- Fraud and Misrepresentation: Financial statements can be manipulated to present an inaccurate picture of a company’s financial position.
Conclusion
Financial accounting is an essential function for any business, providing stakeholders with critical insights into the company’s financial performance and position. By adhering to standardized accounting principles and preparing accurate financial statements, businesses ensure transparency, build investor trust, and meet regulatory requirements. Effective financial accounting helps companies track their financial health, make informed decisions, and strategize for the future.

Interested in what Infinium Suite can do for you?
Links
Contact Us
- +8801714-042726
- info@infiniumsuite.com
- Morning Glory, Concord Colosseum, House# 19 Road No 13C, Dhaka 1213
